7 sampling methods|sampling techniques in statistics examples : distributing There are many different methods researchers can potentially use to obtain individuals to be in a sample. These are known as sampling methods. In this post we share the most commonly used sampling methods in statistics, . Atlético Mineiro Botafogo 的比分直播(和在线视频现场直播.
{plog:ftitle_list}
webCan not load Teamviewer 8 Host onto Mac OS 10.15.7, says teamviewer needs to be updated.
First, you need to understand the difference between a population and a sample, and identify the target population of your research. 1. The populationis the entire group that you want to draw conclusions about. 2. The sampleis the specific group of individuals that you will collect data from. The population can be . See more
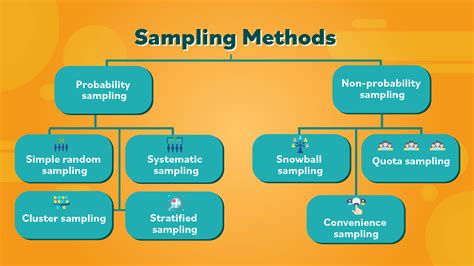
Probability sampling means that every member of the population has a chance of being selected. It is mainly used in quantitative research. If you want to produce results that . See more
types of sampling in biostatistics
type of sampling strategy
In a non-probability sample, individuals are selected based on non-random criteria, and not every individual has a chance of being included. This type of sample is easier and cheaper to access, but it has a higher risk of sampling bias. That means the inferences you . See moreIf you want to know more about statistics, methodology, or research bias, make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples. See more There are many different methods researchers can potentially use to obtain individuals to be in a sample. These are known as sampling methods. In this post we share the most commonly used sampling methods in statistics, . Understand sampling methods in research, from simple random sampling to stratified, systematic, and cluster sampling. Learn how these sampling techniques boost data accuracy and representation, ensuring robust, .
Techniques for random sampling and avoiding bias. Sampling methods. Sampling methods review. Samples and surveys. Choose the sampling method: Select an appropriate sampling method based on the research question, characteristics of the population, and available resources. Determine . A sample is the subset of the population that you actually measure, test, or evaluate and base your results. Sampling methods are how you obtain your sample. Before beginning your study, carefully define the . This tutorial will introduce sampling methods and potential sampling errors to avoid when conducting medical research. Contents. Introduction to sampling methods; Examples of different sampling methods; .
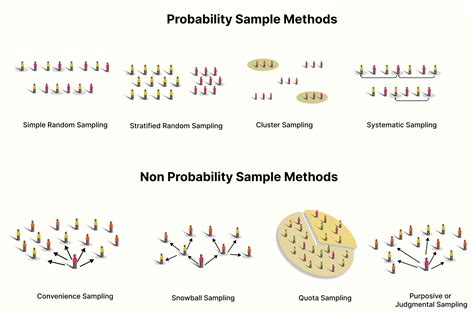
There are two types of sampling methods: Probability sampling involves random selection, allowing you to make strong statistical inferences about the whole group. It minimises the risk of selection bias. Non-probability . Data sampling is a statistical method that involves selecting a part of a population of data to create representative samples. The fundamental aim is to draw conclusions about the entire population without having to engage with every individual data point, thus saving time, resources, and effort while still achieving accurate results.Choosing the right sampling method is a pivotal aspect of any research process, but it can be a stumbling block for many. Here’s a structured approach to guide your decision. 1) Define your research goals. If you aim to get a general sense .
If yes, how should the sampling method change? a. yes b. include all students, not just those graduating Two pills, one sugar and one a new drug, are given at random to two separate groups to determine if a certain drug is effective. Sampling methods are the processes by which you draw a sample from a population. When performing research, you’re typically interested in the results for an entire population. Unfortunately, they are almost always too large to study fully. Consequently, researchers use samples to draw conclusions about a population—the process of making .Lesson 3: Sampling methods. Picking fairly. Using probability to make fair decisions. Techniques for generating a simple random sample. Simple random samples. Techniques for random sampling and avoiding bias. Sampling methods. Sampling methods review. Samples and surveys. Math > Statistics and probability >
A visual representation of the sampling process. In statistics, quality assurance, and survey methodology, sampling is the selection of a subset or a statistical sample (termed sample for short) of individuals from within a statistical population to estimate characteristics of the whole population. The subset is meant to reflect the whole population and statisticians attempt to . Probability sampling methods include simple random sampling, systematic sampling, stratified sampling, and cluster sampling. What is non-probability sampling? In non-probability sampling , the sample is selected based on non-random criteria, and not every member of the population has a chance of being included. We could choose a sampling method based on whether we want to account for sampling bias; a random sampling method is often preferred over a non-random method for this reason. Random sampling examples include: simple, systematic, stratified, and cluster sampling. Non-random sampling methods are liable to bias, and common examples include .Types Of Sampling Methods. Here we will learn about sampling methods, including random sampling, non-random, stratified sampling, systematic sampling and capture/recapture. There are also types of sampling methods worksheets based on Edexcel, AQA and OCR exam questions, along with further guidance on where to go next if you’re still stuck.
sampling techniques in statistics examples
When to use simple random sampling. Simple random sampling is used to make statistical inferences about a population. It helps ensure high internal validity: randomization is the best method to reduce the impact of potential confounding variables.. In addition, with a large enough sample size, a simple random sample has high external validity: it represents the . The researchers chose this sampling method due to its advantages in terms of cost and time constraints, considering the academic nature of the project and the limited timeframe available (Bhardwaj .Simple random sampling. Simple random sampling involves selecting participants in a completely random fashion, where each participant has an equal chance of being selected.Basically, this sampling method is the equivalent of pulling names out of a hat, except that you can do it digitally.For example, if you had a list of 500 people, you could use a random . This denoising process is called sampling because Stable Diffusion generates a new sample image in each step. The method used in sampling is called the sampler or sampling method. Sampling is just one part of the Stable Diffusion model. Read the article “How does Stable Diffusion work?” if you want to understand the whole model.
7 - 4 When random sampling is used, each element in the population has an equal chance of being selected (simple random sampling) or a known probability of being selected (stratified random sampling). The sample is referred to as representative because the characteristics of a properly drawn sample representNMAM is a collection of sampling and analytical methods for workplace exposure monitoring. It includes methods for workplace air, surfaces, and blood and urine. NMAM includes chapters on method evaluation, sampling, and more. NIOSH or its partners have developed or adapted the methods included in the NMAM. NIOSH evaluates the methods according .
Probability sampling is a more reliable way of selecting people for a study because it gives everyone in the group an equal chance of being picked.This means that the findings are more likely to be true for the whole group. Non .
Read more: A Guide to Probability vs. Nonprobability Sampling Methods 5 types of probability sampling Here are the five types of probability sampling that researchers use: 1. Simple random sampling Simple random sampling, or SRS, occurs when each sample participant has the same probability of being chosen for the study. Consider a lottery method. Multi-stage Sampling. This method combines two or more sampling methods, such as cluster sampling and stratified sampling, to create a more complex sample design that is appropriate for the research question and the characteristics of the population being studied. How to conduct Probability SamplingChoosing the right sampling method is a pivotal aspect of any research process, but it can be a stumbling block for many. Here’s a structured approach to guide your decision. 1) Define your research goals. If you aim to get a general sense of a larger group, simple random or stratified sampling could be your best bet. For focused insights or . This sampling technique is also known as judgmental sampling or selective sampling, and it is often used when the population being studied is too small, too difficult to access, or too heterogeneous to use probability sampling methods. Purposive Sampling Methods. Purposive Sampling Methods are as follows: Expert sampling: In expert sampling .
The National Field Manual for the Collection of Water-Quality Data (NFM) provides documented methods and protocols for USGS field personnel who collect water-quality data. The NFM provides detailed, comprehensive, and citable procedures for sampling water resources, processing samples for analysis of water quality, measuring field parameters, and specialized .Sampling is the statistical process of selecting a subset—called a ‘sample’—of a population of interest for the purpose of making observations and statistical inferences about that population. Social science research is generally about inferring patterns of behaviours within specific populations. We cannot study entire populations because of feasibility and cost constraints, . 7: Sampling 7.2: Sampling in Qualitative Research Expand/collapse global location . the point that one should avoid attempting to make statistical generalizations from data collected using quota sampling methods.If you are interested in the history of polling, I recommend a recent book: Fried, A. (2011). .
Sampling is a method that allows researchers to infer information about a population based on results from a subset of the population, without having to investigate every individual. Reducing the number of individuals in a study reduces the cost and workload, and may make it easier to obtain high quality information, but this has to be balanced .
sampling technique in statistics
Sampling is a critical element of research design. Different methods can be used for sample selection to ensure that members of the study population reflect both the source and target populations, including probability and non-probability sampling. Power and sample size are used to determine the num .OSHA Compliance Officers should consult the OSHA Occupational Chemical Database prior to sampling, for current information regarding correct media and flow rates.. OSHA maintains a large number of methods, and in some instances a method may remain available for use, but with different sampling requirements than specified in a given method. Simple random sampling is a probability sampling method where participants within a target population are equally likely to be selected randomly ( Bhardwaj, 2019 ). This technique implies that
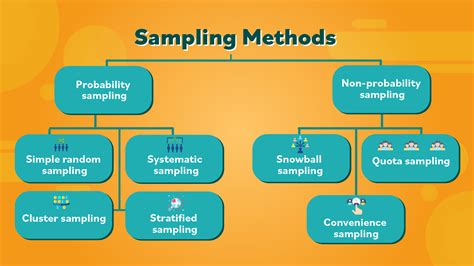
sampling methods for exploratory research
sampling methods byjus
sample example for stats
Resultado da Do you want to play exciting casino games and win big prizes? Join Diamond 777 Bet, the best online gambling platform for fun and entertainment. You can invite your .
7 sampling methods|sampling techniques in statistics examples